Lasers are widely used in the detection field, with rich technical content and obvious impact on social production and life. Laser ranging is one of the applications of lasers. This is because the laser has many advantages such as strong directionality, high brightness, and good monochromaticity.
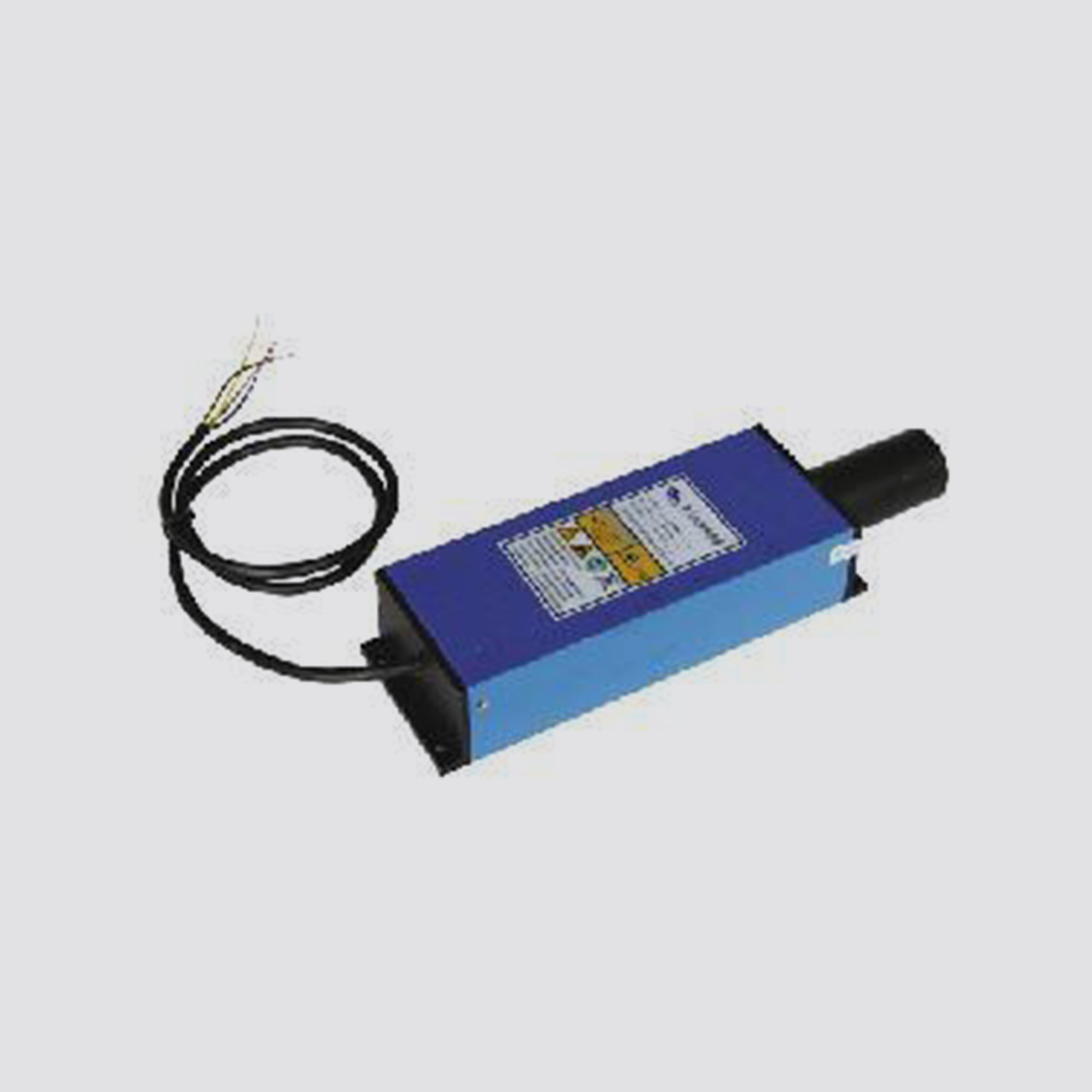

Although laser ranging is simple in principle and simple in structure, it was mainly used in military and scientific research in the past, but it is rare in industrial automation. Because the price of laser ranging sensor is too high, generally in thousands of dollars, now you only need a few thousand RMB for domestic ranging sensors (Shenzhen Quantum Technology Co., Ltd.). In fact, many industrial users are looking for a sensor that enables precise distance detection at longer distances. Because in many cases sensors installed in close proximity are limited by physical location and production environment, today's laser ranging sensors will help engineers in these situations. *working principle
When the laser sensor is working, the laser diode is aimed at the target to emit laser pulses. After being reflected by the target, the laser light is scattered in all directions. Part of the scattered light returns to the sensor receiver, where it is picked up by the optical system and imaged onto the avalanche photodiode. The distance to the target can be determined by recording and processing the time elapsed from when the light pulse is sent to when it is received back. Laser sensors need to accurately measure transit times.
* Solve problems that other technologies cannot solve
Laser distance sensors can be used where other technologies cannot. For example, when the target is very close, ordinary photosensors that calculate the reflected light from the target can also perform a large number of precise position detection tasks. However, when the target is far away or the color of the target changes, it is difficult for ordinary photoelectric sensors to deal with it.
While advanced background noise suppression sensors and triangulation sensors work well with changing target color, their performance becomes less predictable when the target angle is not fixed or the target is too bright. In addition, triangulation sensors are generally limited to within 0.5m.
Ultrasonic sensors are also often used to detect objects at greater distances, and since it is not an optical device, it is not affected by color changes.
The disadvantages of ultrasonic sensors are as follows:
①When the target to be measured is not perpendicular to the transducer of the sensor. Because the target of ultrasonic detection is within the angle of no more than 10° from the vertical azimuth of the sensor.
② When the beam diameter is small. Because the general ultrasonic beam is 0.76cm in diameter when it is 2m away from the sensor.
③ When a visible light spot is required for position calibration.
④ In windy places.
⑤ Vacuum occasions.
⑥ In the case of large temperature gradient. Because this case will cause a change in the speed of sound.
⑦ For occasions where a quick response is required.
 +86-0755-29898410 +86-0755-29898460
+86-0755-29898410 +86-0755-29898460  ron@xaori.net
ron@xaori.net